|
 |
- Search
| J Korean Med Assoc > Volume 47(5); 2004 > Article |
Abstract
Current urologic literatures were evaluated to summarize current status of serum prostate specific antigen (PSA) in the early diagnosis of prostate cancer. Serum PSA is now a routine part of the investigation of men with suspected prostate cancer. While it still has its problems, in particular its lack of specificity, it is a very useful test. Since PSA may overlap in men with and without prostate cancer, other derivatives of PSA were developed to enhance the ability for detecting early stage prostate cancer. This review describes the current status and problems with PSA testing in prostate cancer diagnosis and highlights potential ways in which these may be reduced.
References
1. Smith RA, von Eschenbach AC, Wender R, Levin B, Byers T, Rothenberger D, et al. American Cancer Society guidelines for the early detection of cancer: update of early detection guidelines for prostate, colorectal, and endometrial cancers. Also: update 2001-testing for early lung cancer detection. CA Cancer J Clin 2001;51:38-75.
2. Barry MJ. Clinical practice. Prostate-specific-antigen testing for early diagnosis of prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 2001;344:1373-1377.
3. Catalona WJ, Ramos CG, Carvalhal GF, Yan Y. Lowering PSA cutoffs to enhance detection of curable cancer. Urology 2000;55:791-795.
4. Oesterling JE. Prostate-specific antigen:a critical assessment of the most useful tumor marker for adenocarcinoma of the prostate. J Urol 1991;145:907-923.
5. Benson MC, Whang IS, Pantuck A, Ring K, Kaplan SA, Olsson CA, et al. Prostate specific antigen density: a means of distinguishing benign prostatic hypertrophy and prostate cancer. J Urol 1992;147:815-816.
6. Carter HB, Pearson JD, Metter EJ, Brant LJ, Chan DW, Andres R, et al. Longitudinal evaluation of prostate-specific antigen levels in men with and without prostate disease. JAMA 1992;267:2215-2220.
7. Oesterling JE, Jacobsen SJ, Chute CG, Guess HA, Girman CJ, Panser LA, et al. Serum prostate-specific antigen in a community-based population of healthy men: Establishment of age-specific reference ranges. JAMA 1993;270:860-864.
8. Morgan TO, Jacobsen SJ, McCarthy WF, Jacobson DJ, McLeod DG, Moul JW. Age-specific reference ranges for prostate-specific antigen in black men. N Engl J Med 1996;335:304-310.
9. Oesterling JE, Kumamoto Y, Tsukamoto T, Girman CJ, Guess HA, Masumori N, et al. Serum prostate-specific antigen in a community-based population of healthy Japanese men: lower values than for similarly aged white men. Br J Urol 1995;75:347-353.
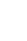
10. Lee SE, Kwak C, Park MS, Lee CH, Kang W, Oh SJ. Ethnic differences in the age-related distribution of serum prostate-specific antigen values:a study in a healthy Korean male population. Urology 2000;56:1007-1010.
11. Ku JH, Ahn JO, Lee CH, Lee NK, Park YH, Byun SS, et al. Distribution of serum prostate-specific antigen in healthy Korean men: influence of ethnicity. Urology 2002;60:475-479.
- TOOLS